Stages of eye cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. The healthcare team uses information from tests to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the organ have cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Doctors may use the stage to help plan treatment and estimate the outcome (prognosis).
Different types of eye cancer are staged differently. Some types of eye cancer aren’t staged at all. The doctor may just describe the cancer by its location and spread. Your healthcare team may use the term advanced when describing eye cancer. Eye cancer is advanced when it has grown outside of the eyeball (called extraocular extension) or has spread (metastasized) to other parts of the body.
Find out more about staging cancer.
Staging melanoma of the eye
Melanoma of the eye is staged differently depending on what part of the eye it starts in.
Conjunctival melanoma and orbital melanoma are not assigned stages. Doctors describe these tumours by where they started in the eye and where they have spread.
Melanoma of the eyelid is staged like melanoma skin cancer in any other part of the body. Find out about stages of melanoma skin cancer.
Uveal melanoma is most commonly staged using the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system. For uveal melanoma there are 4 stages. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the larger the cancer is or the more the cancer has spread.
Sometimes doctors use the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study (COMS) classification system to stage uveal melanoma. This is a simpler system that classifies the tumour based on width and thickness (height). It uses the terms small, medium or large when describing a tumour. The COMS system is used less often than the TNM system.
- Small means the tumour is 5 to 16 mm wide and 1 to 3 mm thick.
- Medium means the tumour is less than 16 mm wide and 3.1 to 8 mm thick.
- Large means the tumour is more than 16 mm wide and 8 mm thick.
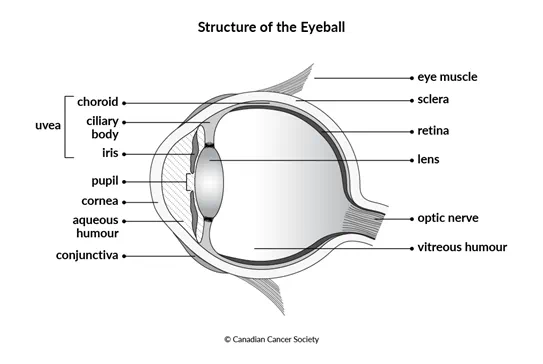
Stages of melanoma in the choroid or ciliary body
The following stages are used for melanoma in the choroid or ciliary body (also called posterior uveal melanoma).
An important part of staging these tumours is the size category (T). The size category is based on the thickness (height) and largest diameter at the base of the tumour. The higher the number, the larger the tumour is.
A size category T1 tumour is either:
- 3 mm thick or less and no more than 12 mm wide
- 6 mm thick or less and no more than 9 mm wide
A size category T2 tumour is one of the following:
- 3 mm thick or less and 12.1 to 18 mm wide
- 3.1 to 6 mm thick and 9.1 to 15 mm wide
- 6.1 to 9 mm thick and no more than 12 mm wide
A size category T3 tumour is one of the following:
- 15.1 to 18 mm wide and 3.1 to 6 mm thick
- 12.1 to 18 mm wide and 6.1 to 9 mm thick
- 3.1 to 18 mm wide and 9.1 to 12 mm thick
- 9.1 to 15 mm wide and 12.1 to 15 mm thick
A size category T4 tumour is one of the following:
- more than 15 mm thick
- more than 18 mm wide
- more than 12.1 mm thick and more than 15.1 mm wide
In the description of the stages below, the cancer is assumed to have begun in the choroid. Posterior uveal melanoma very rarely occurs in the ciliary body without also being in the choroid. If you have posterior uveal melanoma cancer that started in the ciliary body and is not in the choroid, your healthcare team will explain how the cancer is staged for this cancer specifically.
Stage 1
The tumour is size category T1. There is no cancer in the ciliary body or outside of the eyeball.
Stage 2A
The tumour is size category T1. The tumour has grown into the ciliary body but not outside of the eyeball.
OR
The tumour is size category T1. The tumour has grown outside of the eyeball but has not grown into the ciliary body. The part of the tumour that is outside the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour is size category T1. The tumour has both grown into the ciliary body and grown outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour that has grown outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour is size category T2. There is no cancer in the ciliary body or outside of the eyeball.
Stage 2B
The tumour is size category T2. There is cancer in the ciliary body, but it has not grown outside of the eyeball.
OR
The tumour is size category T3. There is no cancer in the ciliary body or outside of the eyeball.
Stage 3A
The tumour is size category T2. The tumour has grown outside of the eyeball but has not grown into the ciliary body. The part of the tumour that is outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour is size category T2. The tumour has grown into the ciliary body and grown outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour that has grown outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour is size category T3. The tumour has grown into the ciliary body but not outside of the eyeball.
OR
The tumour is size category T3. The tumour has grown outside of the eyeball but has not grown into the ciliary body. The part of the tumour that has grown outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour is size category T4. There is no cancer in the ciliary body or outside of the eyeball.
Stage 3B
The tumour is size category T3. The tumour has grown into the ciliary body and grown outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour that has grown outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour is size category T4. The tumour has grown into the ciliary body but not outside of the eyeball.
OR
The tumour is size category T4. The tumour has grown outside of the eyeball but has not grown into the ciliary body. The part of the tumour that is outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
Stage 3C
The tumour is size category T4. The tumour has grown into the ciliary body and grown outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour that has grown outside of the eyeball is 5 mm thick or less.
OR
The tumour can be any size category. The tumour has grown outside of the eyeball. The part of the tumour that is outside of the eyeball is more than 5 mm thick.
Stage 4
Cancer has spread to 1 or more of the nearby (regional) lymph nodes.
OR
Cancer has spread to other parts of the body (called distant
Stages of melanoma in the iris
The following stages are used for melanoma in the iris (also called anterior uveal melanoma).
Stage 1
The tumour is only in the iris and is no more than 1/4 of the size of the iris.
Stage 2A
The tumour is only in the iris but is more than 1/4 of the size of the iris.
OR
The tumour is only in the iris and is causing glaucoma (an increase in eye pressure).
OR
The tumour has grown into the ciliary body but is not causing glaucoma.
Stage 2B
The tumour has grown into the ciliary body and choroid but is not causing glaucoma.
Stage 3A
The tumour has grown into the ciliary body or choroid and is causing glaucoma.
OR
The tumour has grown into the sclera. It may also have grown into the ciliary body or choroid.
OR
The tumour has grown outside of the sclera 5 mm or less.
Stage 3B
The tumour has grown outside of the sclera more than 5 mm.
Stage 4
Cancer has spread to 1 or more of the nearby (regional) lymph nodes.
OR Cancer has spread to other parts of the body (called distant
Staging lymphoma of the eye
Lymphoma of the eye is staged like that type of lymphoma in any other part of the body.
For example, lymphoma of the eye that is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is staged like NHL in any other part of the body. Find out about the stages of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Staging squamous cell carcinoma of the eye
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the eye (conjunctival SCC) is not staged. Doctors describe these tumours by their location and spread.
When SCC affects the eyelid, it is staged as non-melanoma skin cancer. Find out about stages of non-melanoma skin cancer.
Recurrent eye cancer
Recurrent eye cancer means that the cancer has come back after it has been treated. If it comes back in the same place that the cancer first started, it’s called local recurrence. It can also recur in another part of the body. This is called distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
