What is non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a cancer that starts in lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. They are found in the bone marrow, blood and lymphatic system. They help protect the body against germs and abnormal cells, including cancer cells.
NHL includes many different types of lymphoma. But NHL is different from and more common than Hodgkin lymphoma. Hodgkin lymphoma is treated differently than NHL. Find out more about Hodgkin lymphoma.
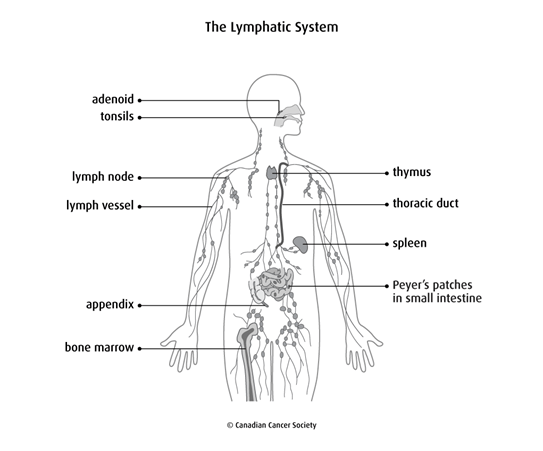
NHL can start almost anywhere in the body, but most types develop in the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is an important part of the immune system. It helps your body fight infection and disease. The lymphatic system is made up of lymph fluid (which carries lymphocytes), lymph vessels, lymph nodes and lymphatic organs and tissues, such as the tonsils and spleen. Find out more about the lymphatic system.
NHL often starts in a group of lymph nodes in one part of the body, such as in the neck, above the collarbone, under the arms, in the abdomen or in the groin.
Types of NHL
There are many different types of NHL. Some types are more common than others, and some are very rare.
The types of NHL are often described by the type of lymphocyte the lymphoma starts in:
- B-cell lymphomas start in B cells.
- T-cell lymphomas start in T cells.
- NK lymphomas start in natural killer (NK) cells.
Each type of NHL is also described and grouped based on how quickly the cancer is growing:
- Indolent lymphomas tend to grow and spread slowly, so they may not cause any signs and symptoms at first. The most common type of indolent NHL is follicular lymphoma.
- Aggressive lymphomas grow and spread quickly. They tend to cause severe symptoms soon after they develop, so they need to be treated right away. They also tend to come back and need more treatment. The most common type of aggressive NHL is diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Sometimes doctors describe the type of NHL by where it is found in the body and by certain genetic changes within the lymphoma cells.
Find out more about the different types of NHL and how they are treated.
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
