Stages of pleural mesothelioma
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. The healthcare team uses information from tests to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the organ have cancer, if the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome (prognosis).
The information on this page is about staging for pleural mesothelioma, which is the most common type. There is no staging system for the other types of mesothelioma (peritoneal mesothelioma, pericardial mesothelioma and mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis).
The most common staging system for pleural mesothelioma is the TNM system. For this type of cancer, there are 5 stages – stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread.
Pleural mesothelioma starts in the
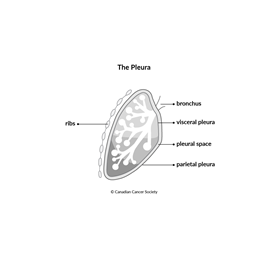
Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging for mesothelioma. Find out more about staging cancer.
Stage 0 (carcinoma in situ)
Cancer cells are only on the surface of the parietal pleura and haven't grown into (invaded) the pleura. Stage 0 is also called mesothelioma in situ.
Stage 1A
The tumour is in the parietal pleura and may have grown into the visceral pleura.
Stage 1B
The tumour is in the parietal or visceral pleura. It has also grown through the pleura and into at least 1 of the following:
- the diaphragm
- a lung
OR
The tumour is in the parietal or visceral pleura. It has also grown through the pleura and into at least 1 of the following:
- the connective tissue (fascia) that makes up part of the chest wall
- the fat in the space between the lungs
- only 1 area of soft tissues in the chest wall
- the mesothelium covering the heart (called the pericardium) – but it hasn’t grown all the way through it
Stage 2
The tumour is in the parietal or visceral pleura. It may have also grown through the pleura and into at least 1 of the following:
- the diaphragm
- a lung
The cancer has also spread to lymph nodes in the chest on the same side of the body as the tumour.
Stage 3A
The tumour is in the parietal or visceral pleura. It has also grown through the pleura and into at least 1 of the following:
- the connective tissue that makes up part of the chest wall
- the fat in the space between the lungs
- only 1 area of the soft tissues in the chest wall
- the mesothelium covering the heart (pericardium) – but it hasn’t grown all the way through it
The cancer has also spread to lymph nodes in the chest on the same side of the body as the tumour.
Stage 3B
The tumour is in the parietal or visceral pleura. It may have also grown through the pleura and into at least 1 of the following:
- the diaphragm
- a lung
- the connective tissue that makes up part of the chest wall
- the fat in the space between the lungs
- only 1 area of the soft tissues of the chest wall
- the mesothelium covering the heart (pericardium) – but it hasn’t grown all the way through it
The cancer has also spread to lymph nodes on both sides of the chest.
OR
The tumour is in the parietal or visceral pleura. It has also grown through the pleura and into at least 1 of the following:
- the chest wall and ribs
- the mesothelium lining the abdomen and pelvis (peritoneum)
- the parietal or visceral pleura on the other side of the chest
- the esophagus, windpipe (trachea) or large blood vessels in the space between the lungs (mediastinum)
- the bones of the spine (vertebrae)
- the spinal cord
- the mesothelium covering the heart (pericardium) and the muscle layer of the heart (myocardium)
Stage 4
The cancer has spread to other parts of the body (called distant metastasis), such as to the lung on the other side of the body, the liver or the bones. This is also called metastatic pleural mesothelioma.
Recurrent mesothelioma
Recurrent mesothelioma means that the cancer has come back after it has been treated. If mesothelioma comes back in the same place, it’s called local recurrence. If it comes back in tissues or lymph nodes close to where it first started, it’s called regional recurrence. Mesothelioma can also come back in another part of the body. This is called distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
