What is gestational trophoblastic disease?
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is the name for a group of rare conditions
that can develop in the
The trophoblast develops after a sperm and egg join. The fertilized egg divides and grows to become a blastocyst. The blastocyst contains an inner mass of cells (called the embryoblast), which normally develops into an embryo and then a fetus. The trophoblast surrounds the embryoblast and connects it to the wall of the uterus. The trophoblast also forms part of the placenta, which is an organ that develops during pregnancy to provide nutrients and oxygen to a fetus as it grows.
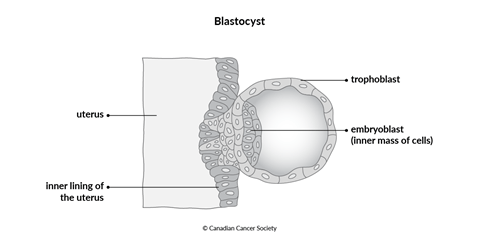
In GTD, the cells that make up the trophoblast don’t develop normally. Instead, they grow out of control and form a tumour.
GTD usually develops just after a sperm and egg join. But it can also occur if trophoblast tissue is still in the uterus after:
-
a miscarriage or abortion
-
a tubal, or ectopic, pregnancy (a pregnancy that happens outside of your uterus)
-
a normal pregnancy
The most common type of GTD is a non-cancerous (benign) tumour called a hydatidiform mole. Doctors may call the presence of a hydatidiform mole a molar pregnancy.
In rare cases, trophoblast cells can develop into a cancerous (malignant) tumour. A non-cancerous hydatidiform mole can also develop into cancer. Cancerous GTD is also called gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN).
Cancerous gestational trophoblastic disease
Non-cancerous gestational trophoblastic disease
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
