The kidneys
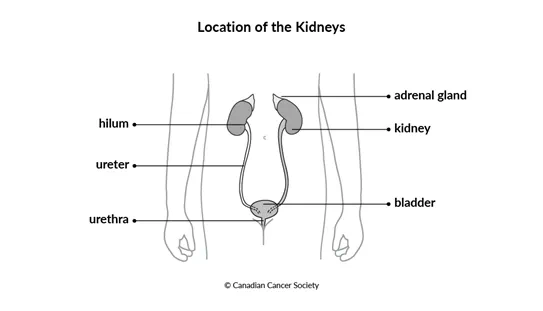
The kidneys are part of the urinary system. There are 2 kidneys in the body, one on
either side of the spine under the lower ribs, deep inside the upper part of the
abdomen. The ureters are thin tubes that connect each kidney to the bladder. They
are about 25 to 30 cm (10 to 12 in) long. The urethra is a small tube that connects
the bladder to the outside of the body. There is an adrenal gland just above each
kidney. The adrenal glands are part of the
Structure
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs. An adult kidney is about 10 cm (4 in) long, 6 cm (2 to 3 in) wide and 3 cm (1 to 2 in) thick. A layer of fatty tissue holds the kidneys in place against the muscle at the back of the abdomen.
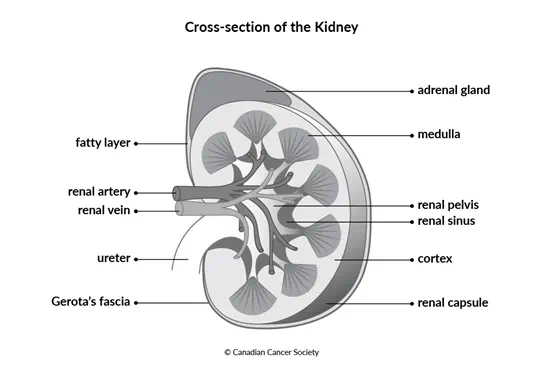
Gerota’s fascia is a thin, fibrous tissue on the outside of the kidney. Below Gerota’s fascia is a layer of fat.
The renal capsule is a layer of fibrous tissue that surrounds the body of the kidney inside the layer of fat.
The cortex is the tissue just under the renal capsule.
The medulla is the inner part of the kidney.
The renal pelvis is a hollow area in the centre of each kidney where urine (pee) collects.
The renal artery brings blood to the kidney.
The renal vein takes blood back to the body after it has passed through the kidney.
The renal hilum is the area where the renal artery, renal vein and ureter enter the kidney.
The nephrons are the millions of small tubes inside each kidney. Each nephron has 2 parts. Tubules are tiny tubes that collect the waste materials and chemicals from the blood moving through the kidney. The corpuscles contain a clump of tiny blood vessels called glomeruli that filter the blood as it moves through the kidney. The waste products are passed through the tubules to the collecting ducts, which drain into the renal pelvis.
What the kidneys do
The main function of the kidneys is to filter water, impurities and wastes from the blood.
The blood from the body enters the kidneys through the renal arteries. Once in the kidney, the blood passes through the nephrons, where waste products and extra water are removed. The clean blood is returned to the body through the renal veins.
The waste products filtered from the blood are then concentrated into urine. The urine is collected in the renal pelvis. The ureters move the urine to the bladder, where it is stored. Urine is passed out of the bladder and the body through the urethra.
The kidneys also act as endocrine glands. They make these
- Erythropoietin (EPO) stimulates the bone marrow to make red blood cells.
-
Calcitriol, a form of vitamin D, helps the colon absorb
calcium from the diet. - Renin helps control blood pressure.
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
