What is acute myeloid leukemia?
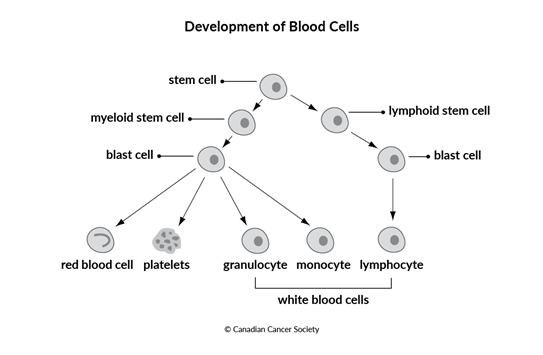
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer that starts in stem cells of the blood. Stem cells are basic cells that develop into different types of cells that have different jobs. As the stem cells of the blood develop, they become blast cells (blasts), which are immature blood cells. In leukemia, there is an overproduction of blast cells. These blast cells develop abnormally and don't develop into mature blood cells. Over time, the blast cells crowd out normal blood cells so that they can't do their jobs. When leukemia is diagnosed, these blast cells may be called leukemia cells.
There are many different types of leukemia. They are grouped based on the type of blood stem cell they developed from. Blood stem cells develop into either myeloid stem cells or lymphoid stem cells.
Myeloid leukemias develop from abnormal myeloid stem cells. Myeloid stem cells
normally develop into different types of mature blood cells –
The types of leukemia are further grouped based on how quickly the leukemia develops and grows. Acute leukemias start suddenly, developing within days or weeks. Chronic leukemias usually develop slowly over months or years.
AML starts in abnormal myeloid stem cells and develops quickly. AML is the most common type of leukemia in adults. It is less common in children.
The blood and bone marrow
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
